Black holes are the most troublesome creatures in the fascinating zoo of the universe. They are the most despicable objects, throwing up unimaginable infinities and unending paradoxes, making physicists the laughing stock of the world. Unable to resolve these paradoxes or contain these infinities, physicists are stuck in a limbo, where they can neither explain and embrace nor reject and discard the existence of these entities. Yet these remain as the most elegant entities, enclasping the extremum, encoding the infinity, and imagining the incongruity.
Last week showed the global recognition of black holes, with the Nobel prize in physics being awarded to people who proved that black holes are an unavoidable prediction of the theory of General Relativity, and also people who discovered the presence of a black hole in the centre of the milky way. But now, out of the blue, what if I tell you that black holes are not really black, but they emit radiation in contrast to their very name…
What are Black holes?
In short, black holes are extremely dense compact objects which form as a consequence of a dying star. The star at the end of its life consumes all of its fuel and stops burning, and starts collapsing under its own weight. Since there is no outward force present to balance, the collapsing goes on and on until all of the mass gets concentrated at a single point in space-time. The event horizon is a surface enclosing this point at a fixed distance from it. The point is called the singularity and its gravitational effects are soo strong that not even light can escape from inside the event horizon.
The event horizon is called the point of no return. Outside the event horizon, matter is still attracted inwards by the singularity but outward accelerations can cause it to move in different directions, even away from the black hole. But once inside the event horizon, the future of the matter is only the singularity, no force can cause it to escape out and its fate is sealed to end up falling into the singularity.

[GIF: NASA]
Black hole entropy paradox.
The universe loves its entropy, and always sticks to the second law of thermodynamics which states that the entropy of the universe is ever increasing and never decreasing. You want to defy this law? Simply throw the entropy into the black hole. You have no ways to measure the entropy of the black hole, it has infinite entropy and any entropy you add into it, it gets eaten into the infinity and is lost. You throw some object into it, the black hole’s entropy remains unchanged and the entropy of the surroundings decreases, thus decreasing the net entropy of the universe, violating the second law. There is no reason that the very loved law of physics is allowed to be broken by the black holes. This was a clear paradox which took the genius of Bekenstein and Hawking to get resolved.
Hawking calculated that the area of the event horizon would increase when some matter falls in. He also noticed that when two black holes merge, the area of the event horizon of the resulting black hole would be more than the sum of the areas of the individual black holes. This looked similar to the case of entropy, the area of the event horizon always increases just like the entropy. This motivated Bekenstain to state that the entropy of the black hole is not infinity but in fact a finite value. This entropy, surprisingly, is directly proportional to the surface area of the event horizon rather than its volume. Any object falling into the black hole would increase its size in such a way that the increase in the event horizon’s area proportional to its entropy. This clearly fits into the model and resolved the entropy paradox, but silently gave rise to a new paradox…
The new paradox…
The fact that the entropy is not infinite but finite should mean that the black hole should not be at absolute zero, but should be having some temperature. And any body that has temperature would emit some radiation given by the blackbody spectrum. But how can something black emit radiation?
This paradox was resolved by Hawking who proposed the theory that every black hole emitted radiation called Hawking radiation which corresponds exactly with the blackbody spectrum. But where does this radiation come from?
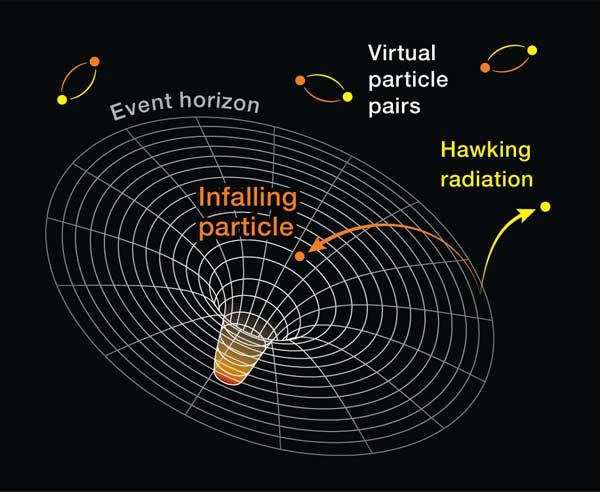
The vacuum is not really empty space but is filled with fields like the electromagnetic field, Higgs field etc. These fields cannot have zero value constantly because then we would know both the value and rate of change precisely and the uncertainty principle prevents exactly this. So there are fluctuations constantly in the values of these fields and the energy is always non zero. What this non-zero energy means is that there is constant excitation of the field in form of virtual particle-antiparticle pairs. Virtual means that these particles cannot be directly observed, but their presence can be verified by their effects. These pairs come to existence randomly and annihilate each other. From the conservation of energy, the particle has positive energy and the antiparticle has negative energy. The antiparticle is short-lived, thanks to its negative energy and hence, within that short period, it has to meet its particle counterpart and annihilate it. This keeps on happening forever in the vacuum, with all sorts of particle-antiparticle pairs popping in and out of existence randomly.
Hawking Radiation…
If you introduce a black hole to the recipe, things change drastically. The gravitational field of a black hole is so strong that even a real particle could have negative energy there. One of the particles from the virtual pair may fall into the black hole. Now there is no one to annihilate its pair on the outside and hence it can escape out to infinity. In this process, it absorbs energy from the black hole and turns into a real particle. To an observer outside, it seems as if this radiation is being emitted by the black hole. The energy of the radiation comes from the black hole itself and as the black hole emits the hawking radiation, it constantly loses mass and gets smaller in size. But the entropy of the emitted radiation is always greater than the entropy lost due to the decrease in size of the black hole and hence the second law is never violated.
The Hawking radiation is mostly photons rather than other particles. This is a real form of radiation. It has real energies and calculable energy distribution for its photons, and you can calculate both the flux and temperature of this radiation based on the black hole’s mass alone. Generally, the Hawking radiation is a long wavelength and low energy radiation.
[{image: Medium]
The fact that black holes emit radiation defies the very definition of black. This gives rise to another paradox, the most perfectly black objects in the universe are not at all black but they do emit radiation. It is right to say that black holes are indeed pandora box of paradoxes, very tempting to open, but suffocating at the same time.
Gaze at the infinite, the universe never ceases to amaze.




[…] the moon, you don’t need to know quantum gravity or General Relativity of gravitational waves or Black Holes. Newtonian Gravity is very much accurate to that stage. This shows that neither Newtonian mechanics […]
[…] could say that 2020 would go down in Space History as the year for Black Holes. Astronomers were able to observe a record-breaking explosion which was by a black hole 390 million […]
[…] field, they have a no. of researches like Physics of the Cosmos, Dark Matter & Dark Energy and Black Holes to name a few. The Hubble Space Telescope has been getting images from very ends of the Universe […]
[…] they go on to form Planetary Nebula and White Dwarf. The star also leave stellar remnants like the Black Hole and Neutron Star which we’ll be discussing about in the […]
[…] of Quantum Physics and General Relativity (Gravity).Let’s talk about black holes first.For a black hole of mass M, the radial distance r = 2MG is known as “Event horizon”. It is that distance from […]
[…] The gravitational pull in its vicinity becomes eventually becomes so great that nothing not even light can escape. This resultant object, which is the black hole, therefore emits no light and no other form of radiation (though it is seen to evaporate radiation called Hawking Radiation). […]
Nice one
Thanks for your kind information
Please write still