We think of time as a long line, i.e. a sequence of past, present and future. But the recent advances in the field of Quantum Gravity makes us rethink time. Time is a strange and mysterious entity. But nowhere in the present equations of Quantum Gravity (which is supposedly the most fundamental and basic theory of the universe) occurs time as a variable.
quantum gravity
The Intuitive Time
quantum gravity
To get to the idea of time, we must first and foremost lose all the ideas of time. What we imagine time, is something like this:
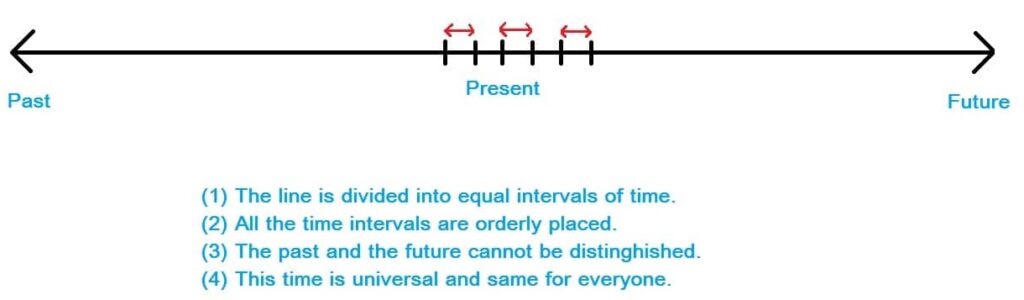
i.e a long line, which is a sequence of instants, which is an ordered 1-Dimensional thing and it has a direction – from past to the future.
The key feature of this idea of time is that it has a past which is fixed. The past is given, we remember it, we know it, we have the traces of the past in books, in history departments, craters of the moon, in our memories, etc. And about the future, we know nothing, it still has to come.
The Problem with Time
quantum gravity
The duration of time elapsed is measured with clocks. If we have two clocks which show the same time, if we take them farther away from each other and then bring them back together they still show the same time. This is the time of our experience. It works as long as we are talking about our daily life. But, it stops working when we look a little bit far ahead from our daily life. The more we look farther, the more properties of time go away.
We consider time as a single thing which has multilayered concepts, i.e the combination of properties. But, if we start removing its properties one by one, what remains is nothing at all. To get along with the modern idea of time, we have to consider four points, some of which we know, and some which we don’t.
1. “Clock measures time”
quantum gravity
We think that all clocks measure time (which is sort of true) and all the clocks go at the same speed (that is not true).
If we take two clocks and take them apart from each other and bring them back together again, if they are good clocks there is quite a probability that they will show different times.
This is because, from Einstein’s equations, mass slows down time. If we take one of the clocks near a black hole and then bring it back to Earth, it will show a different time than the one present on Earth. In our daily routine, we are used to the fact that all the people age uniformly. The difference is very very small, so one does not notice it at all, we are used to it.

So this brings us to the fact that the idea of time as a line is wrong, and the difference between two intervals is not fixed. Thus, there isn’t a single time for everyone.
2. “The meaning of NOW”
quantum gravity
Let’s say I have a meaning of NOW and you have a meaning of NOW. When I look at you and you look at me, do we have the same NOW?
Not really, because it takes time for the light to travel from you to me in the duration when I see you, i.e I see a past you.
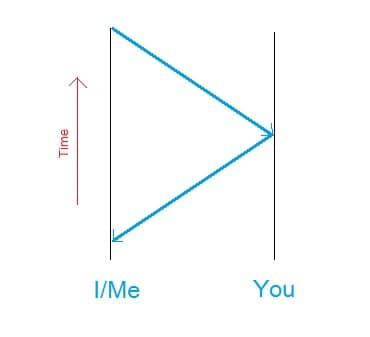
This duration becomes 8 minutes when I look at the sun, 12 hours when I look at Jupiter and more than 4 years when I look at the stars. Between the you I see and the you that sees me, the moment I see you some time has elapsed and that elapsed time can be of order of millions of years if we were situated in different galaxies.
The more you play this game, the more you realise that there is no meaning of “NOW” outside the regime that disregards the time for the movement of light. If we still want to define NOW, we can think of it as a bubble of radii r = cΔt (where c is the speed of light) for Δt in which it can be completely ignored, there is no meaning to NOW outside this bubble.
Thus there is no preferred NOW that you can pick-up. For philosophers, this shook the ground beneath their feet because the very notion of reality of now has to be rethought. The whole idea of “one instance of time” is destroyed. There is no common NOW and no order in a mathematical sense.
3. “Past is different from Future”
quantum gravity
Where does the distinction between past and future come from? The basic laws of physics, i.e the laws of mechanics , electromagnetism, standard model, relativity all do not have the distinction. This distinction between past and future comes from the second law of thermodynamics which states that the entropy always grows towards the future.
Maxwell and Boltzmann stated that this law of entropy is statistical, i.e entropy is not a fundamental quantity, but a measure of how mechanical things are disordered.
Thus, this law also states that the universe in the beginning was highly ordered. That cannot be a coincidence, who prepared it in order? Neither physicists nor philosophers have any answer to that question yet.

Thus the distinction of the future from the past is a macroscopical effect and not a fundamental thing.
4. “Time is Granular”
quantum gravity
This point is not as solid as the first three points because this is not yet proved. General relativity says that there is a connection between time and gravity. Mass affects the flow of time. The understanding of gravity disregards quantum mechanics. That itself is the problem of Quantum Gravity, to merge quantum mechanics with the theory of gravity.
Any clock that measures local time cannot do it continuously, there is a minimal amount of time it can measure, i.e time is ”granular”. The shortest grain of time should be of the order of Planck time, i.e. about 10-44 seconds. And the clock should be in a superposition of different positions of hands and there is a probability distribution for the passing of time from one instance to the other.
Everything about Time
quantum gravity
Everything we know about time disappeared when we went to the most basic level of science. At the basic level, time is any of the ways of counting the change of something. For example, you can make time as the counting of the rise of the moon and sun. Aristotle said that time is a number of changes of some event. Few years later Newton said that time is “change” plus “something else”. That something else is a uniformly flowing thing, i.e time always flows in a certain fashion even if nothing happens.
After that, Einstein came along with his theory of general relativity and called that “something else” as the gravitational field which is a dynamic entity made out of 4D space-time.
When we try to mix general relativity with quantum mechanics, the idea of Newtonian time explodes and nothing remains. The only thing that remains of time is the definition given by Aristotle (the event of counting). Time is not ordered in a line but it is scattered granules like the Aristotle which are connected to one another in some way.
You can follow one bit to another bit and on and on and define the certain event/process as a series of such bits. That is the only thing that remains (i.e the minimum notion of time) when you remove all of its properties at the fundamental level. All of this shows that time is macroscopic, it is not fundamental. This is the reason that in quantum gravity (which we consider as the most basic theory) does not contain any time variable.
quantum gravity



