Japan is famous for its technology and rather I would say fast or superfast technology and now-a-days quantum technology. Whether it is transportation or computing; Japan has always led its way over all other countries around the globe. Recently with its mind-blowing speed of 415.5 petaflops; able to do trillions of calculations in blink of an eye; and a hefty price tag of 48-crore; Japan’s Fugaku is the world’s fastest supercomputer. The one thing powering this incredible machine is Quantum Bits.
Before discussing the newly synthesized chemical molecules which can be potential breakthrough in Qubits; let’s briefly know what actually qubits are for a quantum tech.
Qubits – The rise of quantum tech
For simplicity, we can say that they are carrying unimaginable amount of information in almost no amount of space. They are the basic unit of quantum information or quantum version of the classical binary ‘bit’; physically realized with a two-state device. In classical computing, everything is based on numbers ‘0’ and ‘1’. Thus, while processing info. bit is implemented to any of the one level. Whereas while considering qubits, it can be coherent superposition of both. This way it can hold more amount of info (as infinite superpositions possible).
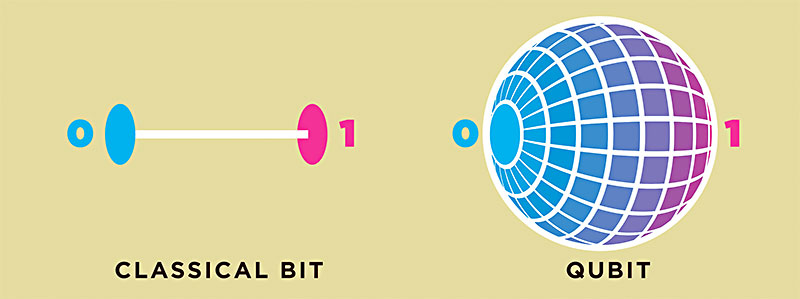
(image: The Austin Chronicle)
Generally, qubits are made of same semiconducting material as usual electronics materials. But now for the first time chemists and physicists at Northwestern University and University of Chicago have developed a new method to create tailor-made qubits. This was done by chemically synthesizing molecules that encode quantum information into their magnetic or ‘spin’ states.
Molecular Qubits that respond to light
Spins in solid state such as quantum dots and defect centres in diamonds, can easily be controlled by light and can be used in quantum information processing. Here, the more challenging part is tuning their properties and making large arrays & this probably can be done easily with spins in molecules.
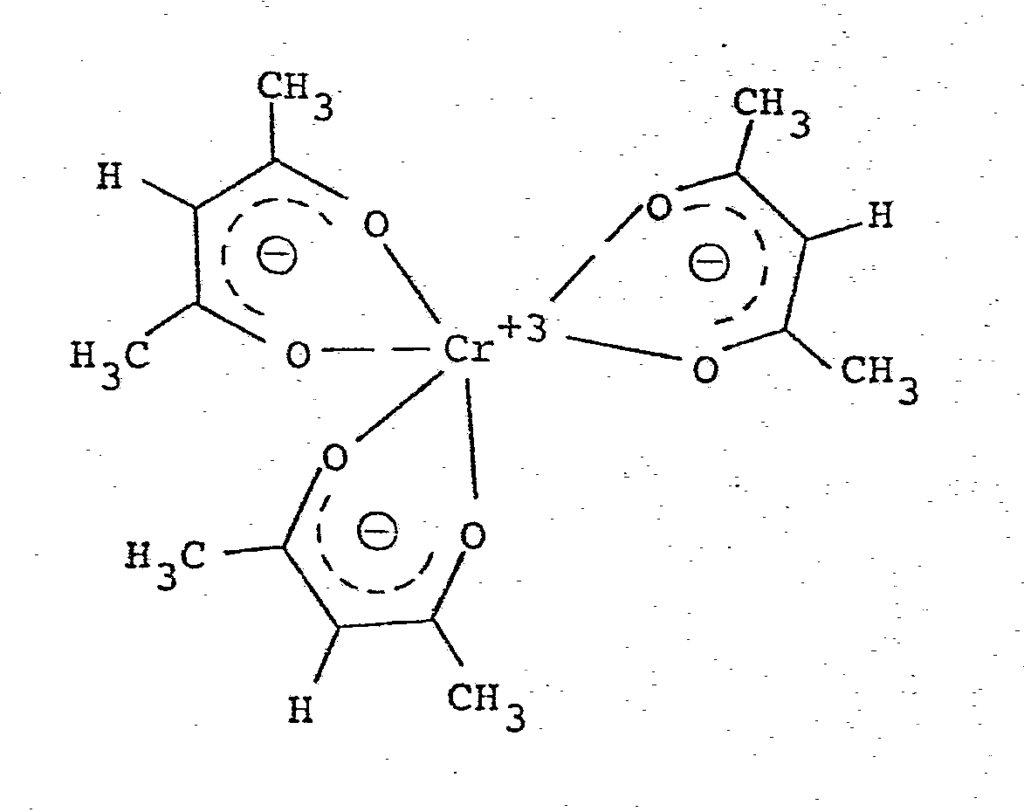
explaining spin and magnetic properties
(image: Google Patents)
For instance, molecules consisting of central Chromium atom, surrounded by organic ligands (ligands are simply the other molecules attached to central atom). The spin and optical properties of this complex can be tailored easily by just changing the positions of the methyl groups on the ligands.
Thus, this depicts that molecules which have tunable properties; especially spin and magnetic; are promising building blocks in quantum tech. Also, at the same time they can be easily assembled into scalable arrays and readily fitted into different devices. In typical molecular systems, addressing ground-state spins would enable wide range of application in quantum tech and information technology. However, this important functionality is difficult to find and not yet achieved.
Researchers have finally found a new bottom-up approach to develop molecules whose spin states can be used as qubits and can be instantly inculcated in the outside world.
Exciting the molecules…Varying the atoms…Producing the ‘Bright Qubits’
In this bottom-up approach, chemists and physicists used organometallic Chromium molecules to create a spin state that they could control with light and microwaves. They typically demonstrated such optical addressability in a series of synthesized organometallic Chromium (IV) molecules.
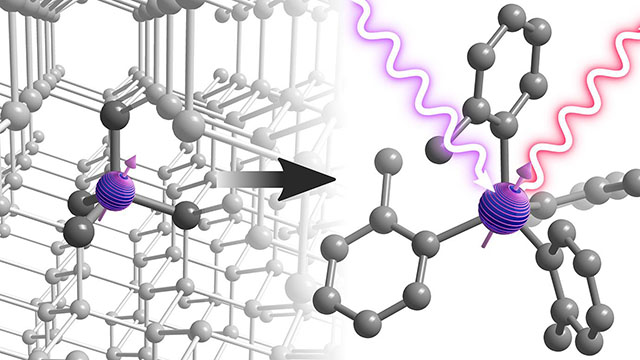
By exciting the molecules with precisely controlled laser pulses and measuring the light emitted; scientists could actually ‘read’ the spin states in the molecules after being placed in a superposition. This particular information is the key requirement for using them in quantum tech. In addition to this, by atomistic modification of the molecular structure, they could successfully vary the spin and optical properties of these compounds. And as I indicated earlier that this is the important functionality difficult to find – which was achieved here.
This highlighted the promise for tailor-made molecular qubits and a new step towards designer quantum systems synthesized from bottom-up approach.
The Achievement for Quantum Tech
“Over the last few decades, optically addressable spins in semiconductors have been shown to be extremely powerful for applications including quantum-enhanced sensing. Translating the physics of these systems into a molecular architecture opens a powerful toolbox of synthetic chemistry to enable novel functionality that we are only just beginning to explore,” said on of the researchers.
This research has potentially opened up the new era of synthetic chemistry. Also, the bottom-approach offers both, functionalization of individual units as ‘designer qubits’ for target applications; and creation of arrays of readily controllable quantum states, opening the possibility of scalable quantum systems.
One major application of such tunable ‘bright’ qubits could be quantum sensors. They can be designed to target specific molecules or could find specific cells within the body or detect when food spoils or even spot dangerous chemicals.
Thus, this new step towards quantum tech could ultimately lead to quantum states that have extraordinary flexibility and control which in turn paves the way for next generation quantum technology. Importantly, this bottom-up approach could also help integrate quantum tech with existing classical technologies. Certainly, the techniques of molecular designs to create new atomic-scale systems for quantum information science can be harnessed. Bringing these two sciences together will surely broaden the interest and has potential to enhance the quantum sensing and computation.
Interestingly in the past, using molecular systems in LEDs was a major transformation in the era of modern electronics – and something similar could be expected with molecular Qubits synthesized here.
This has laid the basis of wickedly strong future of quantum computing with its minuteness and created a paradigm for quantum information science.
—OSD
To read about how quantum computing and quantum information technology has evolved in modern times. Click Here.



Hi there, I enjoy reading all of your post. I wanted to write a little comment to support
you.
Hello, i think that i saw you visited my blog so i came to “return the favor”.I am trying to find things to enhance my website!I suppose its ok to use some
of your ideas!!
May I simply just say what a relief to discover someone who really
knows what they’re talking about online. You certainly realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important.
More and more people must check this out and understand this
side of the story. I was surprised you’re not more popular because
you surely possess the gift.
I have been reading the posts, and I absolutely concur with what Sam said.