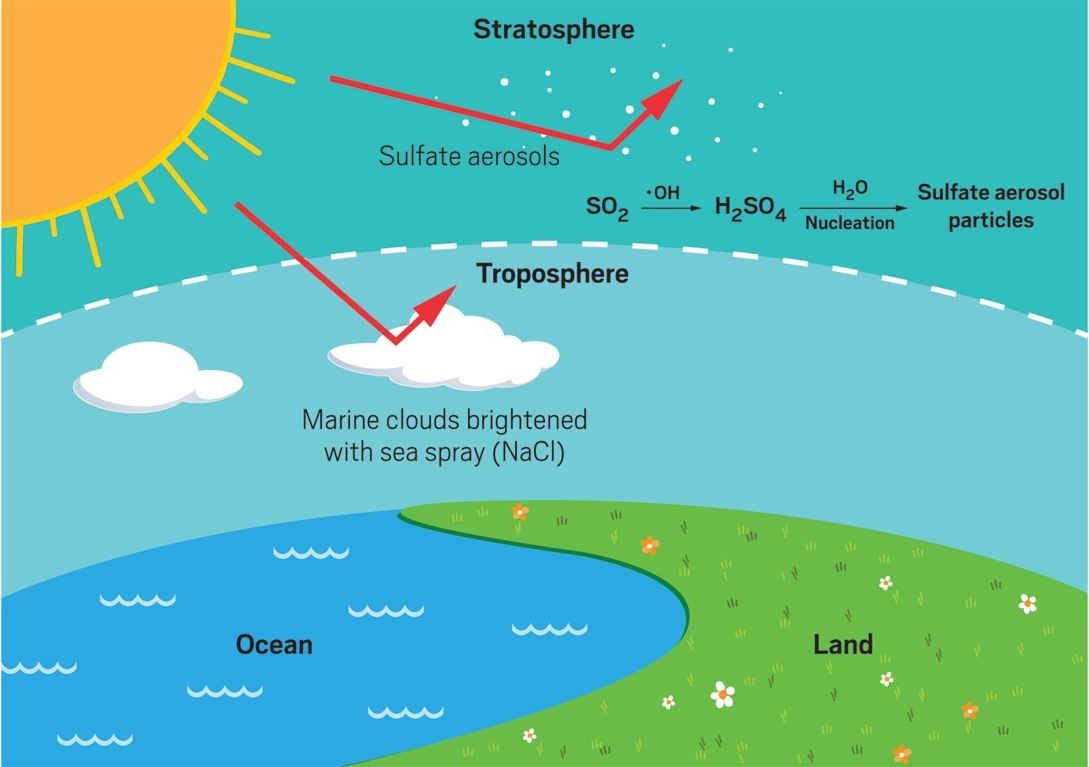
COVID-19 or the Coronavirus disease 2019, caused by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome CoronaVirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has become a severe pandemic. Wuhan province of China happens to be the epicentre of this disastrous outbreak which reportedly took place in November 2019. Since then, treatment and cure for this disease remain the utmost priority among researchers not only from medical sciences but also among chemists, material scientists, synthesis researchers and others.
COVID-19 is a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused by a novel coronavirus that has confronted humans for the first time, consequently, humans need intrinsic immunity to battle against this unique strain of the coronavirus which directs towards severe miscommunication amongst health care departments.
SARS-CoV-2 is highly communicable and assumed to be spread with contact with an infected person, surfaces, and air droplets through the mouth, nose, and eye. It has a lengthy incubation phase of about 14 days and exhibits primary symptoms comparable to common seasonal virus infections like fever, dry cough, and tiredness with trouble breathing. However, as the virus spreads in the body, it can cause severe pneumonia with infection and fibrosis in the lungs and end in respiratory collapse due to disorganised gas transfers that drive various essential organs (heart, kidney, liver, GIT, and brain) failure and a person can die if artificial oxygen is not rendered on time.
Nanotechnology is Being Employed in Multiple Areas
Nanotechnology could play a dormant part in multiple fields like health, defence, farming, and many more. As of now, in the published literature, nanotechnology will lead a pivotal role in inducing interdisciplinary methods of producing affordable, secure, and impactful means for the analysis and therapeutics of several chronic diseases. This aspect review clarifies the modern progress of nanotechnology for the apprehension and treatment
of viral infections with a focus on coronaviruses particularly regarding SARS-CoV-2.
The Potent of Nanomedicine in COVID-19

By the time mentioned, there is no approved therapy for the treatment and doctors have attempted many techniques to control the indications with subsisting drug molecules such as Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine, Ribavirin, Favipiravir, Galidesivir, thalidomide, Emtricitabine, Tenofovir, Baricitinib, Remdesivir, Ruxolitinib, Darunavir, Camostat, Fingolimod, Umifenovir, Lopinavir, and Ritonavir. These drug molecules oftentimes suffer from weak solubility, permeability, and absence of targetability that drives them to malfunction in exerting the aspired therapeutic effect.
Nanotechnology has proven its role in medicine to deliver the drug at the target site with minimal side effects. Several nanotechnology-based
products are currently on the market and are under clinical investigation.
Nanomedicine has many faces that can be accurately employed to deliver the drug molecules to infected cells, and the targeted ligand conjugated nanoparticle explicitly binds with epitopes of the virus that produces inactivation of the virus, inducing it to fail to penetrate the cells. Thus, the infection can be neutralized with nanomedicine-based approaches.
Various nanocarriers have been utilised for drug delivery to resolve the difficulty linked with drug molecules. These can be split into two categories, polymeric and inorganic nanocarriers. In multiple research labs around the world, scientists are working on nanoparticle-based vaccine products which are still in considerations, such as Novavax developing a protein subunit of a nanoparticle vaccine + matrix M (adjuvant) (based on recombinant SARS-CoV-2 glycoprotein). The University of Tokyo/ Daiichi-Sankyo is working on the RNa based lipid nanoparticles (LNP)-encapsulated mRNA for the SARS-CoV-2 infection-causing viruses. Similarly, The Scientific Research Institute of Vaccines and Sera, Saint Petersburg is working on a nanoparticle vaccine.
Nanomedice in Diagnosis of Covid-19

Amidst the COVID-19 crisis, there is an urgency to develop diagnostic kits for the quick detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection to limit the movement of the infectious person. Numerous laboratory-based tests like chest computed tomography, RT-PCR and point of care examinations like detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV19 have been developed. This test can be utilized by medical professionals based on acute and chronic the phase of the viral infection.
The productiveness of the test depends on different factors like the invasive character of the infection, and the advancement of antibodies against antigens presented by the virus in the human body. Nanotechnology has performed a notable position in the fabrication of diagnostic tools at various levels such as sidelong flow assay. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy-based detection where metallic nanoparticles have a fundamental role in improving the signal of analytes and its discovery by optical, electrical and immunofluorescent approaches.
Several nanocarriers are under investigation to improve the conventional drug delivery systems to effectively target drug releases, low dose, reduced toxicity, improved permeability, and controlled release of the drug. Moreover, nanomedicine has also performed significant parts in creating point-of-care testing to tackle infectious diseases like COVID 19.
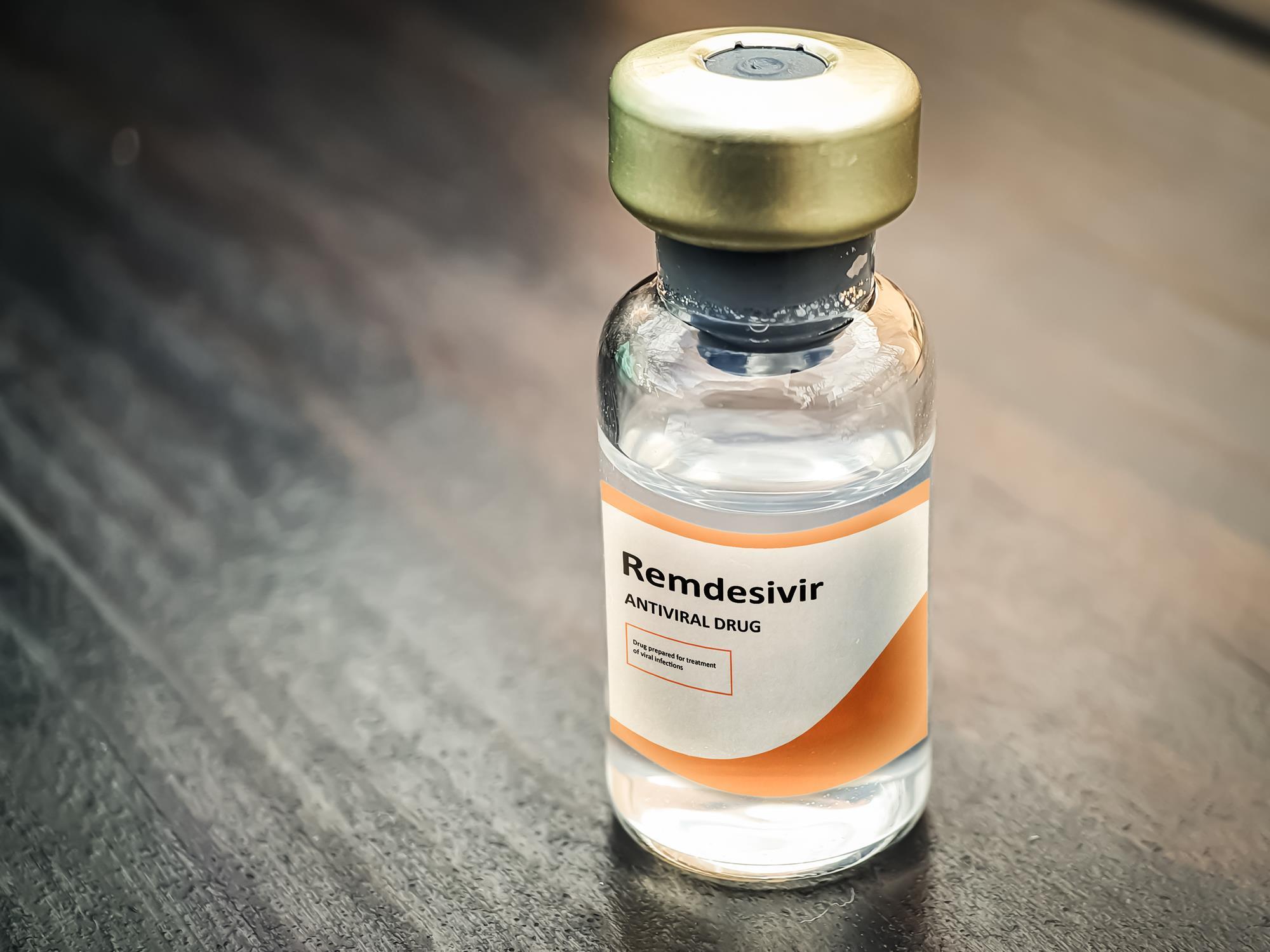

Cyclodextrin based Remdesivir formulation is one of the great successes of nanomedicine in the treatment of COVID 19 infection.






























































/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/12901251/carbon_engineering.jpg)