Phase-A
Data, data, and data! This word is not merely a word but the heart of a Trillion-dollar industry.🤑 Wherever there is money involved, Laws are obligatory! That’s why the Government came up with Privacy Policy which are like the fundamental flexbox grids. Every company has to adhere to it while making designs and decisions which can affect your Privacy.
But why am I talking about this? Why does the title look like more of a warning? The industry which these specifically targeted questions point at is…..(drumroll! 🥁) Quantum Computing. Let’s dive right in to exploit a sinister typical Hollywood plot, shall we?

Devices of the Future or Doom of the User
While this may look like some James Bond Movie device, it’s a computer, to be more specific Quantum Computer. These devices are some of the most amazing and remarkable innovations that have the potential to change human history. But we would be naïve If we ignore the flip side of the coin!
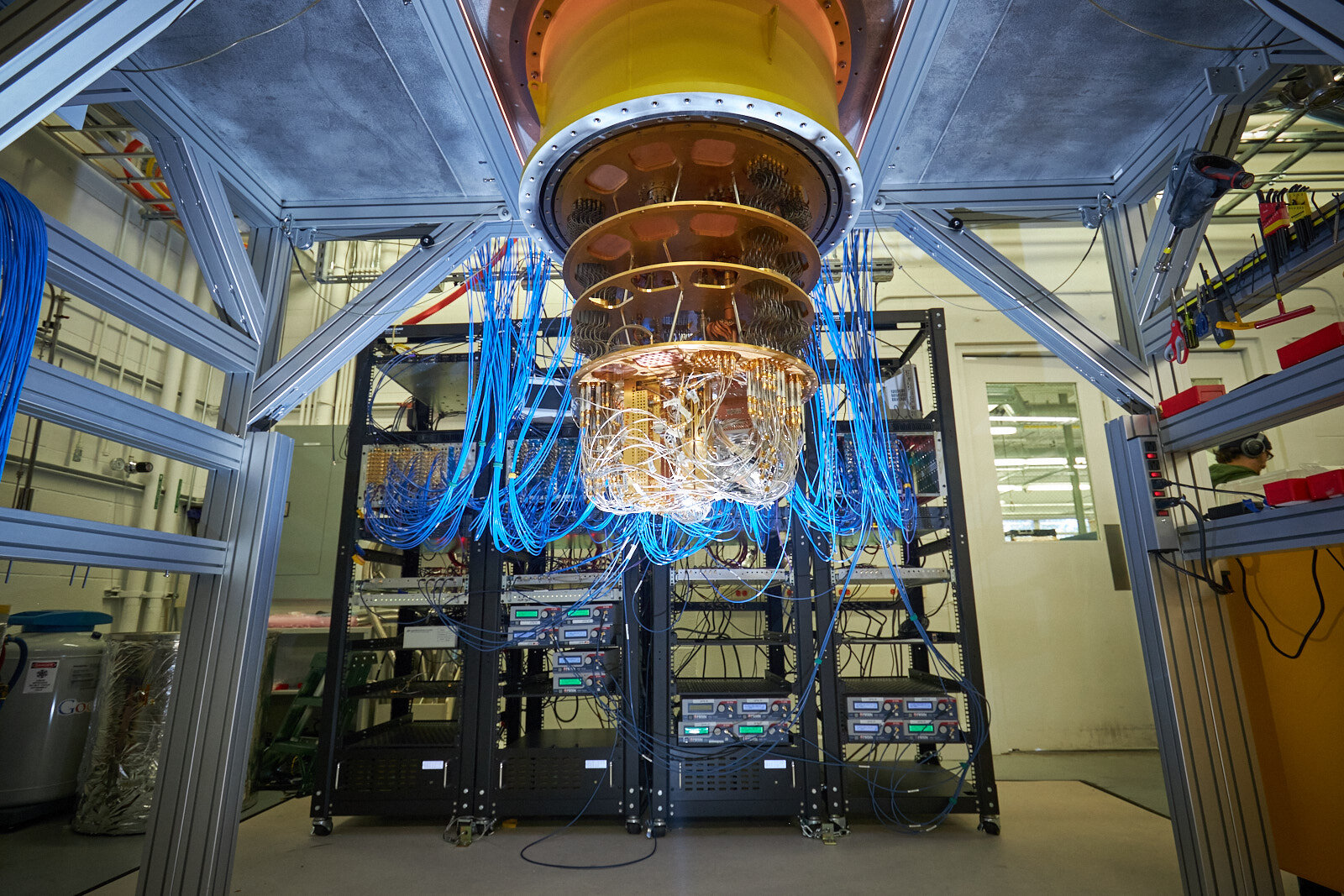

With just the right mix of Quantum physics, Quantum maths, and some electricity, it can crack any of the encryption algorithms used today blowing our privacy into chunks. Don’t worry about safeguarding your data right away, there’s still some time to go! To understand the aforementioned warning we need to understand a bit about this Device. (Doomsday Machine!)
Understanding Quantum Computer Bit by Bit
Everything needs a carrier to carry something important. Just like a body needs hemoglobin to carry oxygen around, a classical computer needs bits to carry data. The size of data that a machine can process at a time determines its speed. So each bit can carry some information with them.
So what makes Quantum so ‘Special’? its principles mainly: Quantum superposition and Quantum entanglement! I will take you through a quick tour. (godspeed!) Superposition is the possibility of being in different states at the same time. Simplifying, a bit which represents 0 or 1 in the classical sense does not exist like that in the quantum sense. In the quantum realm, it exists in the form of 0-1 simultaneously called a “Qubit”. It is a perfectly balanced state between 0 and 1.

Now imagine, both computers are solving a maze. The classical one will try every possible escape route one at a time. Contrarily, quantum one would try all the escape routes at the same time. That gives Quantum an advantage over classical. In normal computer 2 bits can be in a state of (00,01,10,11), with each bit occupying affixed identity. Similarly, qubits can also represent those states with exception of being all the possible states at the same time. So as we add more qubits to the system the power of computation increases exponentially.
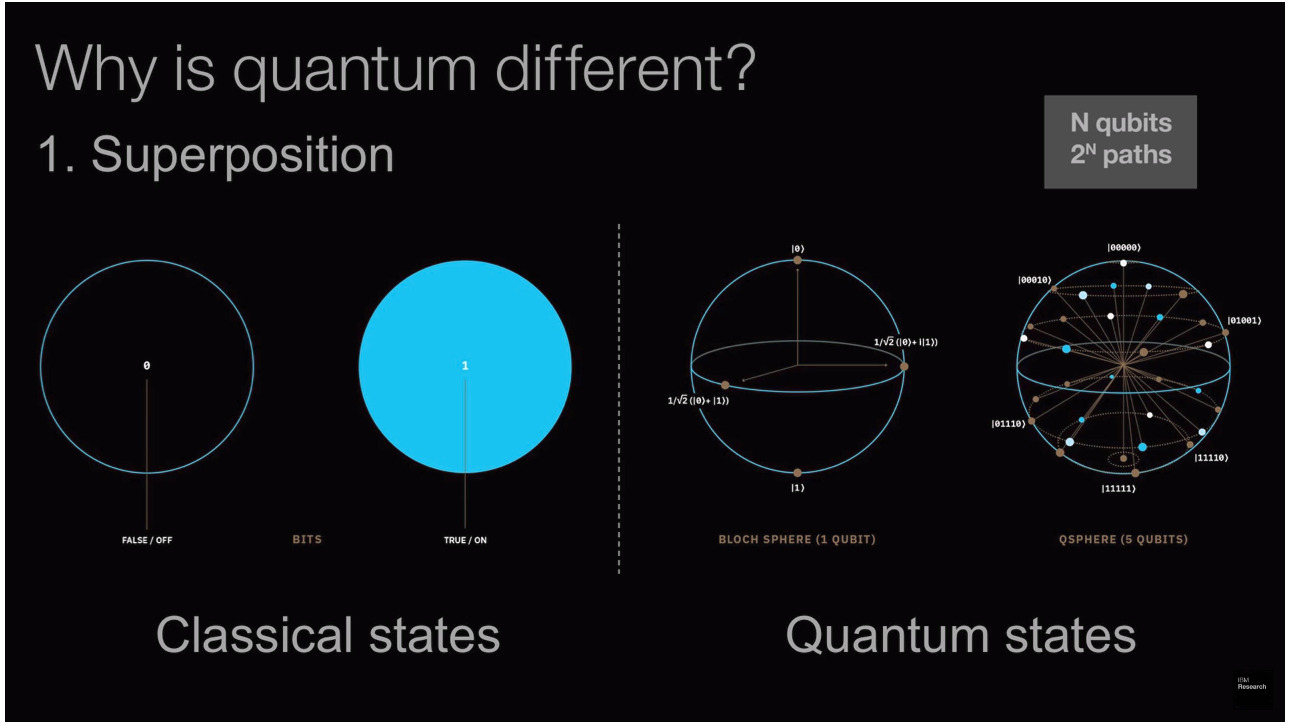
For the exponential boost, you need some sort of nitro. What is the nitro? It’s dubbed famously as “Spooky Action at a Distance.” Entanglement is here to untangle the problem. (Bad joke!! 😝) Just like every team needs some sort of communication, Entanglement provides the same to qubits. Entanglement is also necessary for other experiments like this- Blackhole one. Now to work properly, we need states which cannot be described as a product of two single-particle states.
|↑⟩1|↑⟩2+|↓⟩1|↓⟩2; This is known as Bell State.
Preventing Privacy from Piracy
There are 17 billion devices connected to the Internet today! All of them need some kind of protection, a shield from attacks! To prevent a third party from eavesdropping on your conversation, there are various encryption algorithms deployed for our safety.
To explain subtly, suppose you are talking to your friend and an unknown is standing beside him. If you want to convey something important, you would lower your voice, might even whisper close to your friend. So the third person can’t hear anything or even if he would, it would sound like some sort of gibberish. This is the most simple if not an effective example of encryption.

I won’t write about all the encryption methods here because breaking them into easily understandable parts is tough, as they are you know “Encrypted”! We will explore the RSA algorithm which Q.C specifically aims at breaking. RSA found its widespread use in public key encryption-decryption. This algorithm relies on using a public key and private key for encrypting and decrypting messages.
Decrypting the Working of RSA Algorithm
I’m gonna take you through the working, godspeed! But I know you will catch the gist of it. The algorithm works on principles of pure maths and logic. Assume that you are the recipient and someone is a sender. You will give each sender a virtual lock (public key provided by you) and only the key (private key) which unlocks it remains with you. The sender will use a virtual lock when sending anything confidential to you and you will be able to access it through the key. Easy, right!


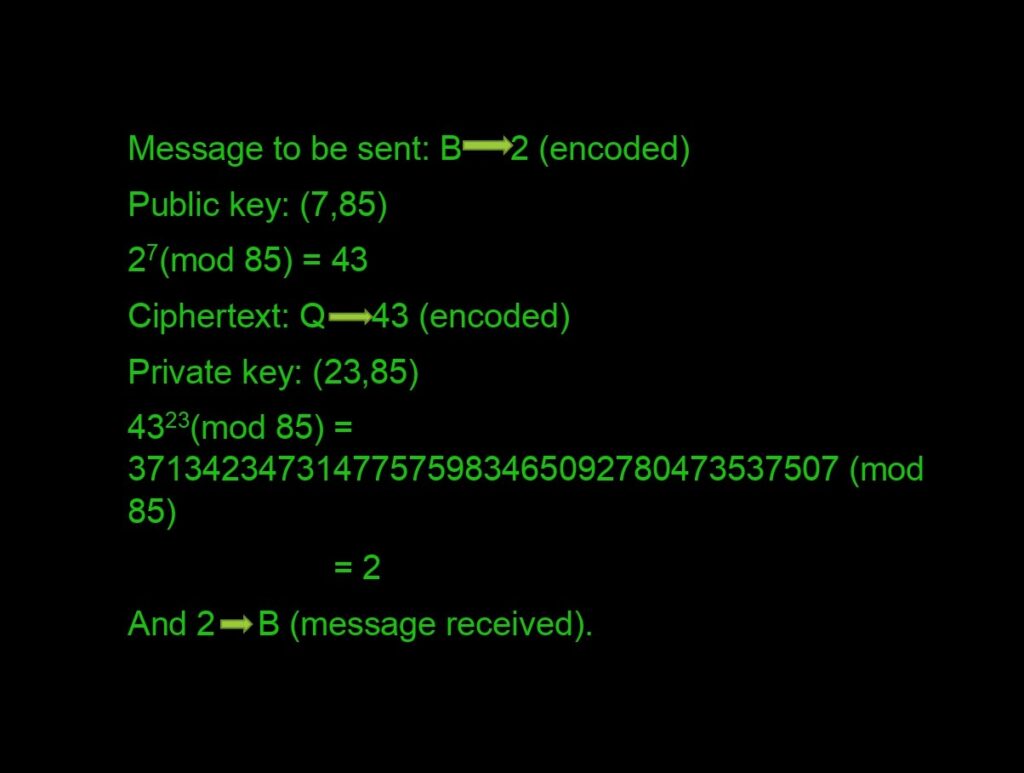
What are the virtual lock and virtual keys? The public key (virtual locks) is based on a number computed from very large two distinct prime numbers along with an auxiliary value. Be ready for some maths that will blow you out of water. Take any two prime numbers, say 5 and 17. (in practice these are very large!!) We assign p=5 and q=17 such that N=p*q=85.
Starting from 1 till N-1=84, we need numbers that do not share a factor with N or are Co-Prime. There is a total of 64 numbers. (Refer to this video here.) Practically it’s not possible to count all of them, so we have a method Φ=(p-1)*(q-1) which gives you all the Co-primes. Next, we compute something called “Carmichael’s Totient Function”. In this, we compute Λ(N)=lcm(p-1,q-1)=16 and is kept secret.
Now we choose ‘e’ such that 1<e< Λ(N) and ‘e’ is Co-prime with Λ(N) and N. In this case 1<e<16, let’s take e=7 where gcd(e, Λ(N))=1. Now we have our lock which is: (7,85). Just one more step, bear with me, we need to compute another factor ‘d’ such that (d*e)(mod N)=1. Skipping all the procedures we get d=23. So now we have our Private key: (23,85).
Seeing the Big Factor at Play for Privacy
Here comes the fun part!! (Hacker mode on!) The big question is how can we break this encryption? The process seems easy at first but it seems to get more and more tricky as it starts to unfold. The reason I mentioned RSA is that the whole diegesis revolves around two main characters: ‘p’ and ‘q’. These primes are kept secret because these are materials that make the lock and key.
We know N is the product of these 2 primes so it can have only 4 factors namely 1, itself, p, and q. Somehow we can find the factors, boom, all the privacy blows to poof! How do you find such large factors? Not by brute force but a Lightsaber that can cut through any lock.

We will discuss the Lightsaber in another article! Let me know in the comments your views on the Government’s privacy policy. Till then stay safe physically as well as digitally.
It is possible to invent a single machine which can be used to compute any computable sequence. And perhaps one day will be able to simulate a human’s Mind.
Alan Turing
Second part of this article is Published. Click Here to crack the RSA Algorithm.




[…] To read about how quantum computing and quantum information technology has evolved in modern times. Click Here. […]
Too good article….nice way to present such complex things !
[…] of quantum computing and the very basics of the RSA algorithm. I mentioned something about the Lightsaber if you can recall. Can’t recall here’s a link. (In case! […]
The memes was something new and wonderful. It added to the essence of the article. Enjoyed this one a lot…😅
Thanks, man! A little inspiration from here and a little from you.😎😂
What a fun read! Such a good way to present this topic.
Thanks, Bhavya! Pleased to read such good responses! 😊
It has been an informational blog and I am glad to know about the quantum computer and more with these amazing memes and analogies used by the author
Thank you so much, Naman, I’m glad the memes worked out amazingly! ✌
Stay tuned, another part is coming! 😉