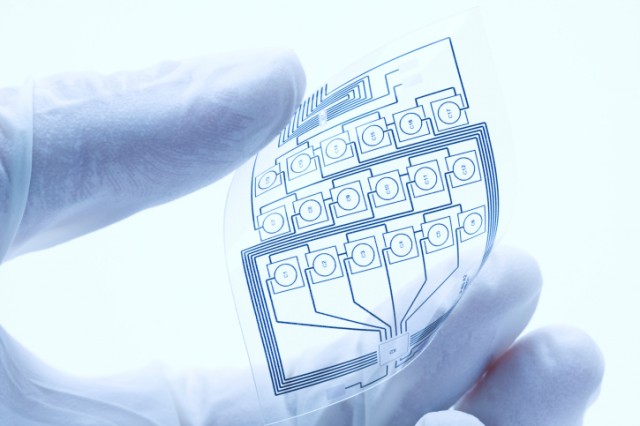
Electronics is one of the many fields which has been witnessing large scale evolutions. This field was once known for its heavy, bulky and rigid devices, which are now replaced with lightweight, soft and flexible appliances. Flexible electronics is an emerging and revolutionary technology having the potential to upgrade conventional electronics and avail ease of recycling, low-cost, flexibility, lightweight, and easy to use.
Deposition Method
The mainly used deposition techniques to develop flexible devices are Screen printing, Ink-Jet printing, Photolithography, Soft Lithography, Doctor blading, Spin coating, etc. The roll to roll process is used to fabricate such devices for large area and low cost.
Applications
It has applications in various societal sectors:
- including healthcare
- the automotive industry
- human-machine interfaces
- mobile communications and computing platforms
- embedded systems in both living and hostile environments
Market-specific applications, such as human-machine interactivity, energy storage, and generation, mobile communications, and networking.
To enable all these applications, electronic devices need to be flexible, lightweight, transparent, stretchable, and even biodegradable. They can fulfill these requirements and are thus becoming increasingly important to next-generation electronic device platforms.
Flexible Electronics: Present and Future
Silicon technology has led the way towards miniaturizing devices, increasing cost-effectiveness, and improving its performance. But the material rigidity of silicon poses a threat to the ubiquitous use in soft electronics (flexible and stretchable electronics) applications. As a result, the research community is in an extensive search of prospective material that has the potential to overcome the drawback of rigidity.
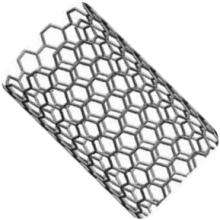
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene prove to be useful for such applications. These materials overshadow silicon in areas of elastic properties, electronic, optoelectronic, and thermal properties. The discovery of nano-carbon materials has created a scope for advancements in soft electronics and has set a trend in the technical world.
Transition-metal dichalcogenide (TMD) materials and boron nitrides are non-Carbon graphene-like 2D materials that have also gained significance in the field of soft electronics.
These materials are deployed in countless applications, but still, there are a few limitations due to the lack of high yield assembly processes. The orientation of CNTs has to be in a specific direction along with desired density and chirality. Large-area manufacture of graphene is achievable, but the damage during the transfer to a substrate hamper the device performance. Hence, finding efficient techniques for assembling CNTs and transferring graphene is one of the hot topics in the research domain.
In the coming future, we expect the industry to witness a fusion of wearable technology with flexible electronics. The progress in the field of Organic sensors would contribute to the commercial availability of features like gesture recognition, contactless control, and biometric sensor arrays.
Stretchable silicon will be a broad topic of research as nano-carbon materials will be unable to match the speed of silicon. The existing LED, LCD technology might affect the growth of flexible electronics, still, the foundation for a new era of electronics has been laid, and this Ubiquitous technology would be here to stay.
To read more about such amazing technology and advancements in electronics. Click Here.





[…] not limited to light hydrocarbons. Carbon black/activated carbon, carbon fibres, fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, and graphene are other products that can be obtained by processing waste. Now, there are multiple […]
[…] Science has always been interesting and so is the field of wearable devices these days. A lot of research is going on each day in this area and lot of technology is developing […]
[…] most awaited technology of the decade, future of electronics: Rollable Displays. Flexible electronics have been in the talk for a long time but commercial viability still seemed far from the truth. But […]
[…] be cheaply and perfectly printed using inkjet and transfer printing. Finally, manufacturing tough Flexible electronics can be cost-effective, energy-saving as well as streamlined. (read more about it […]
[…] major application of such tunable ‘bright’ qubits could be quantum sensors. They can be designed to target specific molecules or could find specific cells within the body or […]
[…] technology in the future. But on the bright side, Graphene is being used to create a new class of Flexible Electronics, de-salination films and much […]
[…] in terms of sensitivity and consistency. Naturally, with these results, future of printed and flexible electronics will be flourished. This is because, coffee stain printing technique provides results exceeding the […]
Good going