Thought this year may have been a bad one for some, it wasn’t the same in the field of Astronomy & Astrophysics as we were able to witness many new findings and events throughout the year, starting with the dazzling first image taken of the Sun by the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (click here to see them) and ending the year by witnessing the closest Great Conjunction in 397 years. Astronomy & Astrophysics had tons of new discoveries and theories that help us reach to getting an better understanding of various astronomical events and objects.
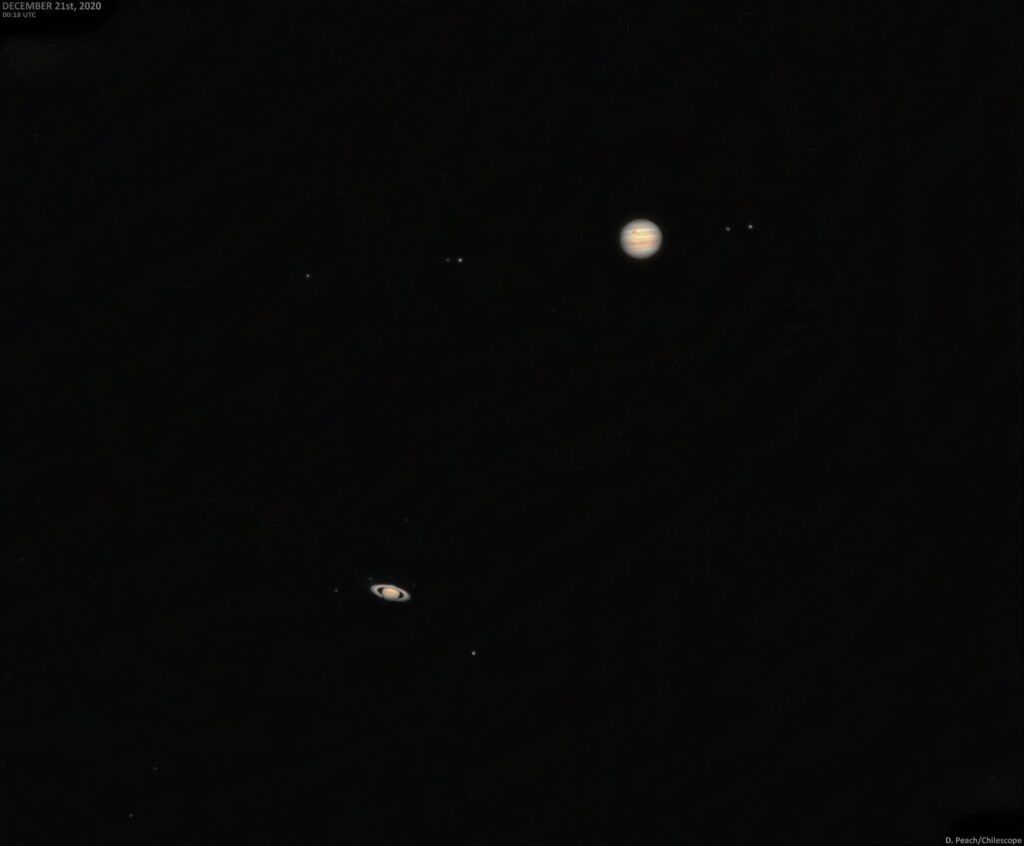

1. The Great Conjunction that amazed the Astronomy Community
We all were able to witness a rare and once in a lifetime astronomical event, Great Conjunction, where Every 20 years, Jupiter and Saturn appear the closest to each other or one could say they appear as one in the night sky. The main reason why the Great Conjunction is special this year as we were able to witness the closest Great Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn with a difference slightly less than 0.1 degree since 1623 which is a 397 years back.

Fun Facts about the Great Conjunction
- The last closest conjunction was in1623., during the time of Galileo
- The last time that the conjunction was visible this close was back in 1226 which is 794 years back.
- The next closest conjunction between the two planets will be in 2080, 2417 and 2477
- The actual average frequency of the Great Conjunction is 19.86 years
- As this year’s conjunction is before Christmas, it known as the “Christmas Star” or the “Bethlehem Star”. Some religious scholars also believe that the Star of Bethlehem that led the Three Wise Man to the location of Jesus’s birth was none other than the Great Conjunction. Though others believe that the Star of Bethlehem was supernova explosion or a comet.
- The Great Conjunction is also known as the “kissing stars” or “double planet”
- Another phenomenon in the Great Conjunction is the Triple Conjunction where occasionally Jupiter appears to pass Saturn three times, in a zigzag pattern. This is actually an illusion caused by Earth’s own movement around the Sun. The most recent Triple Conjunction was back in 1980-81.
2. Asteroids delivered to Earth
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hayabusa2 Mission successfully dropped off its sample collection capsule on December 6 in Australian Outback. The capsule contained samples from the Near-Earth Asteroid 162173 Ryugu (meaning “Dragon Palace”) that was collected earlier this year. The sample is one of the first subsurface materials that’s been ever collected from an asteroid. The Hayabusa2 is now moving on to visit other asteroids to collect samples.
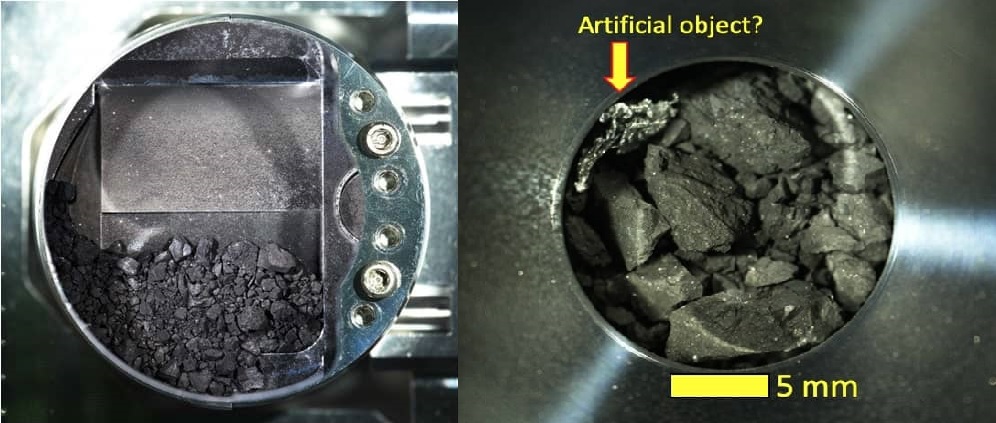
The interesting part is that asteroid Ryugu is an ancient fragment of a larger asteroid that formed in the cloud of gas and dust that spawned our solar system. It is rich in carbon, which is an element essential to life making it a very interesting asteroid. The samples from this asteroid will help us get a better understanding on how the solar system was formed and the origin of water on Earth.
Prior to the Ryugu delivery, JAXA’s Hayabusa mission brought back tiny samples of Asteroid 25143 Itokawa back in 2010 as part of the first asteroid sample-collecting mission in history. Also in 2006, NASA were successfully able to collect a small sample from comet Wild-2 under the Stardust mission.
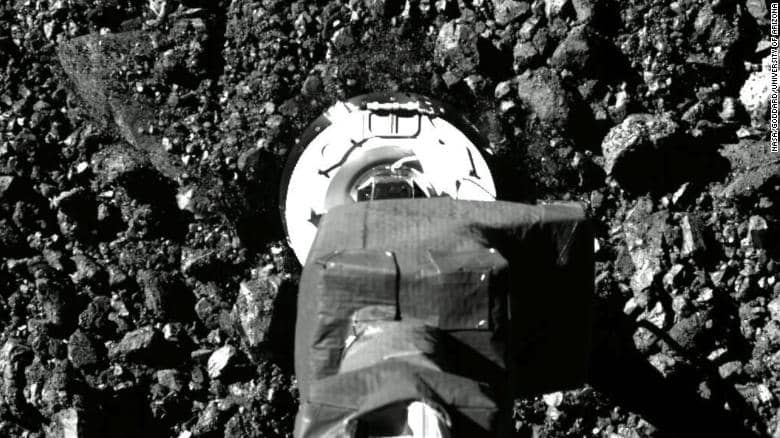

NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission briefly landed on the near-Earth Asteroid 101955 Bennu and successfully collected a sample from the asteroid’s surface that will be delivered back to Earth by 2023
3. Black Holes in the Spotlight
We could say that 2020 would go down in Space History as the year for Black Holes. Astronomers were able to observe a record-breaking explosion which was by a black hole 390 million light-years away from Earth. The explosion was the biggest explosion detected in the Universe, with some also comparing it the 1980 Mt. St. Helens volcanic eruption.

The biggest spotlight was that the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded for black hole discoveries that revealed the darkest secrets of the Universe.
Astronomers were also able to witness the spaghettification of a star as it was shredded and devoured by a supermassive black hole. They also found the closest black hole to Earth which is about 1000 lightyears away.
European Southern Observatory (ESO)]
They also discovered the long-sought intermediate-mass black hole, the size which is between that of a small black hole and a supermassive black hole. This discovery will help us get a better understanding on how black holes evolve. This observation of an intermediate-mass black hole is now known as IMBH.



