Humanity has been on a war with Nature since the era of Industrialization. Now, the threat of Climate Change looms over civilization as a Sword hung on strands of rope. Our current precarious scenario seems to haze the facts that are lying in front of us. While the strands appear to lose the forces that clutch them.
However, we might have something that can buy us crucial time before the inevitable disaster. A Cheat Code to hack nature- Geoengineering!
What Exactly is Geo-Engineering?
The growing years have made it clear that we won’t be shifting anytime soon from fossil fuels. But, Geo-engineering may buy us some time before we can start the ‘Great Transition.’

Geo-engineering typically encompasses two very different conceptions: First is Carbon Capture, sucking CO2 out of the air so that less heat is trapped. The second is blocking excess sunlight from entering the atmosphere, so less heat is absorbed in the first place. The first one is known as “Carbon Removal” or “Negative Carbon Emissions.” Modern researchers tend to differentiate between the two aforementioned terms. And the second one is probably known as Solar-Geo-engineering.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/12901251/carbon_engineering.jpg)
It refers to planetary-scale technology to counteract the global rise in temperature. There are many technologies proposed under this blanket term like seeding clouds with reflective particles, dissipating heat-trapping clouds, or scatter sunlight in the stratosphere.
The origins of Geo-engineering came up in 1965 when the scientific advisory committee to President Lyndon Johnson mentioned the need to inject reflective particles to offset the sunlight. But the best plausible solution in solar geo-engineering is ‘Stratosphere Aerosol Injection.’
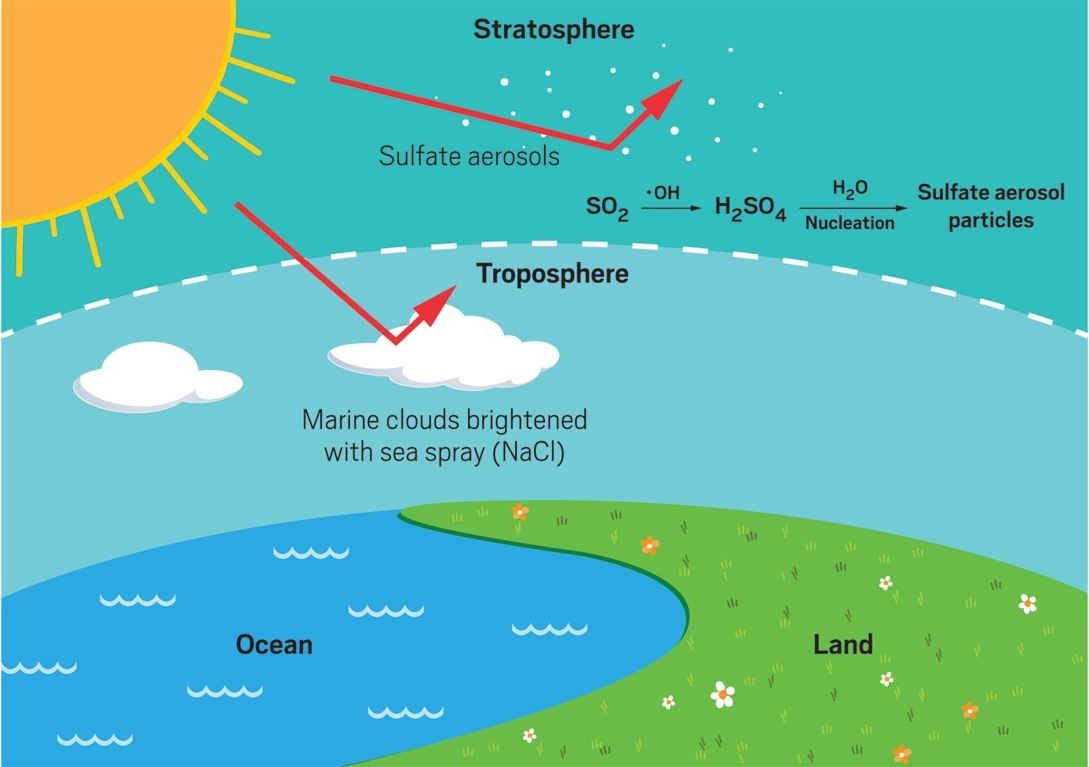
Stratosphere Aerosol Injection
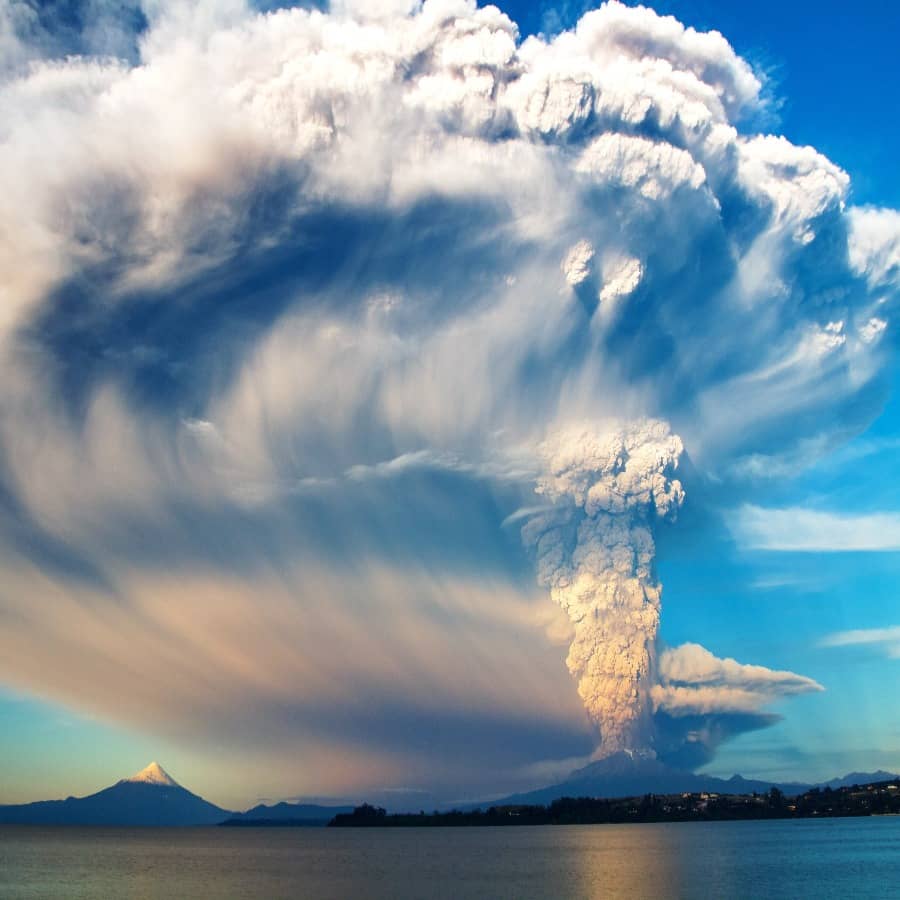
The underlying technology behind this terminology is scattering sunlight in the stratosphere so less heat is absorbed. The idea seemed far-fetched until 1991 when nature demonstrated the practical aspect of this experiment.
The 1991 Mount Pinatubo Volcanic Eruption. It was the second-largest eruption of the 20th century that spewed out large amounts of materials and killed over 900 people. But, scientists noticed the dramatic effects of this tragedy on climate. The eruption spewed roughly 42 to 234 Mt of CO2 and 15 to 19 Mt of SO2. The eruption was so massive that the cloud reached as high as the stratosphere (around 12-20 km) and the particulates stayed there.
The SO2 ejected into the stratosphere formed a slight haze of gaseous sulfuric acid clouds. And that thin veil of sulfuric acid blanket covered the entire stratosphere reducing global average temperatures by 0.5°C. It took 3 years until this cooling effect subsided, which inspired scientists to think that they could perform such a feat artificially.

What makes it more interesting is that we can do this experiment with the current technology we possess. Although many researchers argued the ways to spray aerosol particles in the stratosphere. The aircraft-based delivery system seems to be the most probable and efficient solution. Many engineers said that it’s possible to use cargo planes or even fighter jets, a study published by Wake Smith and Gernot Wagner mentioned the opposite. They highlighted in the paper that current cargo airplanes cannot fly at such a high 20km altitude, nor the fighter jets that can fly at this altitude can sustain it long enough.
They proposed a specially designed aircraft called ‘SAIL’ (Stratospheric Aerosol Injection Lofter). The cost of making a modified aircraft was hinted at around $2.1 to $5.6 billion. The fleet would grow to start with 8 aircraft in the first year to 95 in year-15. The model assumed cutting the rate of temperature change by half from the first-year forward. The amount of SO2 to be spewed is estimated at roughly 0.1 Mt S yr-1 with an increase of 0.1 Mt S yr-1. Though many studies showed that ideal amounts would be 5-8 Mt yr-1 staying constant around that figure. Finally, the overall cost of the large-scale experiment is estimated to be around $2.24 billion per year.
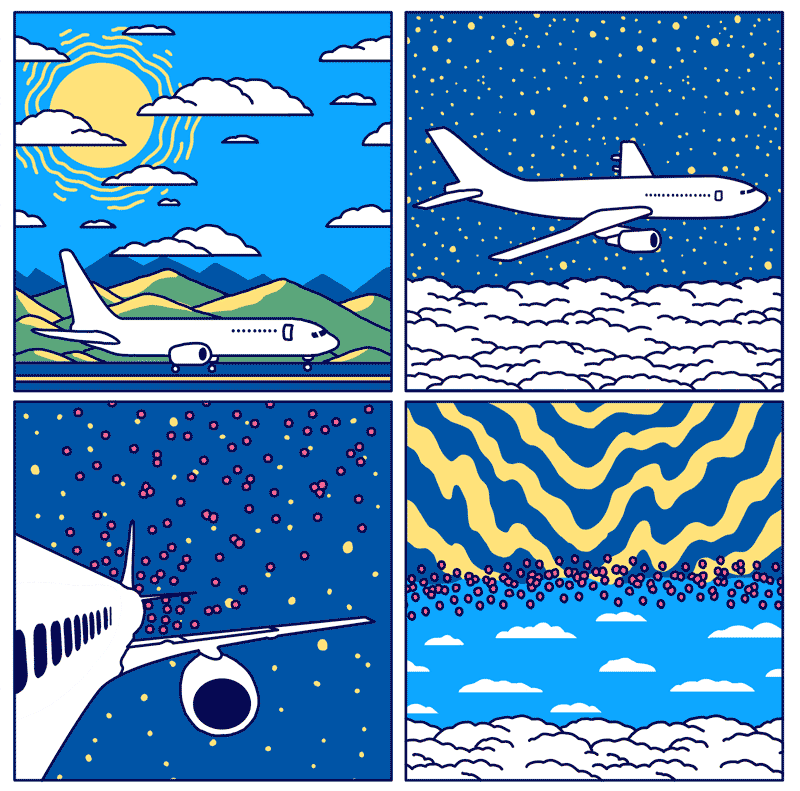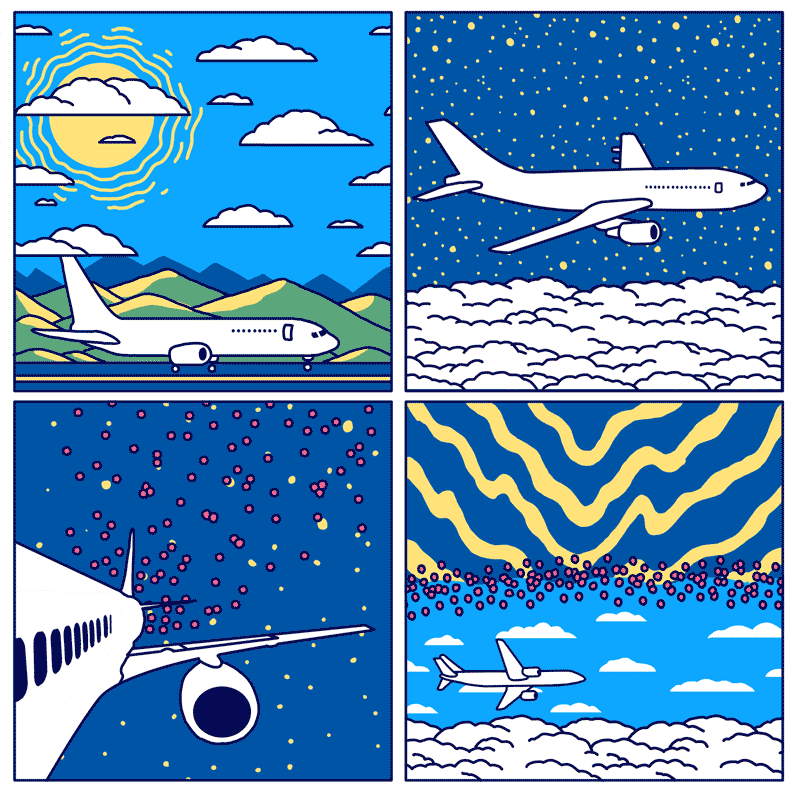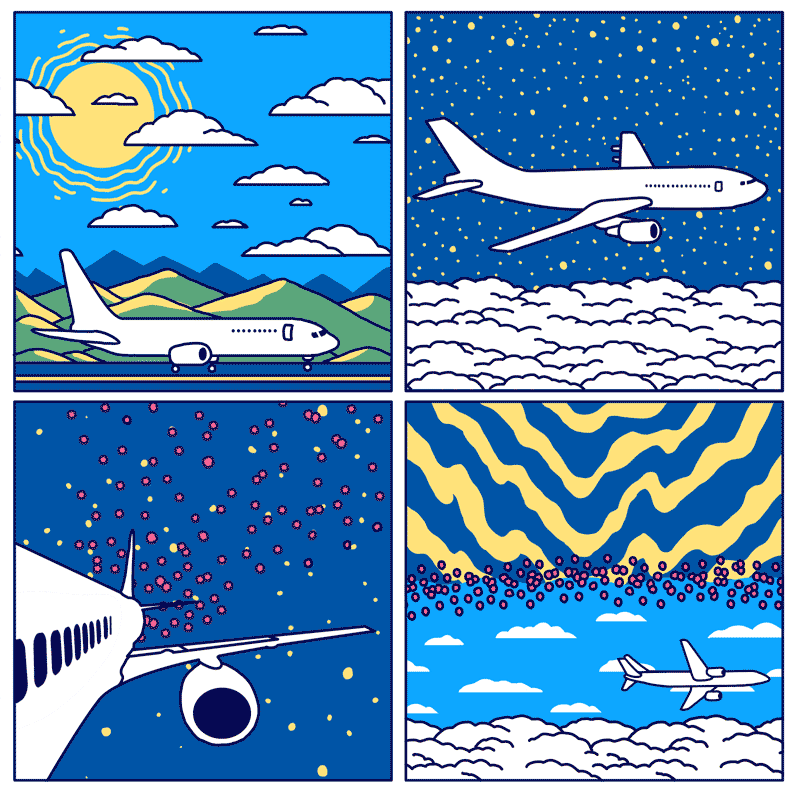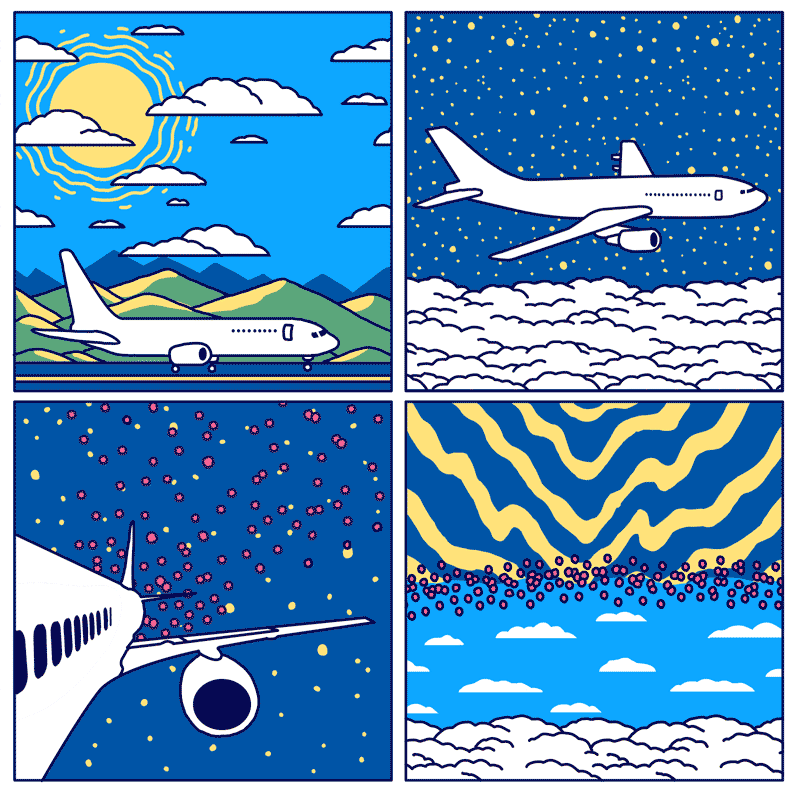
However, when you mess with such a huge complicated system termed ‘Climate’, no variable can estimate the probability of success of this experiment.
Should We Be Doing Geo-engineering?
We have been a silent witness to one of the most treacherous experiments in humanity- CO2 Geo-engineering. For the past 3 decades, humans have been running a rather horrible experiment to see how fast Climate changes if we add approx. 40 billion tonnes of CO2 per year. Though it would be idiotic to say and point out this fact.
A professor at Harvard University David Keith has been studying Geo-engineering for the past 20 years and mentions that more research is needed to amplify the consequences of this hack. Until unless we conduct a large-scale experiment we might never be able to confirm the theoretics of the predicted model.
[the_ad id=”7507″]
An independent study on the effects of SO2 injection landed on the conclusion that we might end up on the wrong path. They mentioned that releasing such an amount of SO2 would heat up the stratosphere not the earth more profoundly. Creating a veil of acid could increase the chances of acid rain and acidify oceans more than ever. The drop in temperature would affect rainfall and wind patterns across the globe. The SO2 would penetrate the ozone layer more than ever.

However, once we start to pump the aerosols into the atmosphere we might be forced to do so for a long time, otherwise, we would have to face a “Termination Shock.” After 30 years, when we decide to cease the Geo-engineering venture, the natural cycle would take over again. But this time the heated stratosphere would push the temperature catastrophically above par. The temperature would skyrocket by 2-4 k. An increase that would take 50 years naturally would just take 10 years. Such a severe shock would disrupt all the natural ecosystems providing them no window to adapt.
Highlighting the Controversies
An environmentalist, Dru Jay, says, “You have one planet and you are risking the whole planet for that experiment.” On the contrary, David Keith adds that “Doing Geo-engineering has risks but not doing it has even more risks.” The climate change problem isn’t gonna go away even if we cut our emissions by zero in the next decade or so. Even if we are to perform such an experiment we need the governments of all countries on board. But a substantial quandary is ‘Whose hand is gonna be at the knob?’. Every political leader has that aspiration to assume the God-Like Mantle. Then how would the community address this political enigma?

Kristine Tomkins a Conservationist says “I don’t believe that technology is some sort of technofix that will fix the technology [Industrialization] that got us here in the first place.” So, what does this mean to our approach towards Climate Change? Is it better to leave things alone, or should we intervene in something beyond our limit? Is it too late to start? “I guess we will never know if we don’t start something and sometime soon!“
[the_ad id=”7507″]
References:
- Sources of Geo-engineering: https://sites.google.com/view/sourcesgeoengineering
- MIT Technological review on Geo-engineering: https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/08/09/615/what-is-geoengineering-and-why-should-you-care-climate-change-harvard/
- Mount Pinatubo Eruption: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pinatubo/self/
- Facts of Mount Pinatubo: https://web.archive.org/web/20100120022421/http://www.tetontectonics.org/Climate/SO2InitiatesClimateChange.pdf
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2009GL039209
- Costs of SAI: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aae98d/pdf
- Fine-Tuning Climate | DW Documentary: https://youtu.be/b1Enrzgrl1w
- Geo-engineering | Kurzgesagt: https://youtu.be/dSu5sXmsur4




[…] Dioxide Removal/ Carbon Capture and Storage and Solar Radiation Management. You can read more about SAI and CCT in the previous […]
When someone writes an paragraph he/she keeps the plan of a user in his/her brain that how
a user can know it. Therefore that’s why this post is amazing.
Thanks!