It is known to us that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating, rather than slowing down due to gravity. This expansion is said to be caused by Dark Energy, which is said to composes about 68% of the Universe, but even though it is so abundant, its nature is beyond understanding for physicists as of now.
Dark Energy was first observed by examining the light from extremely distant signals like supernovae. When scientists measured the distance and red shift, they concluded that the Universe isn’t made up of matter and radiation only, but also a new form of energy that would change the fate of Our Universe.
What is Dark Energy?
Dark Energy is an unknown and hypothetical form of energy that affects the Universe by producing a negative gravity or anti-gravity i.e. it acts against gravity. This is being theorized from the observable properties of distant supernovae, which show that the universe is expanding at an accelerating speed. Like Dark Matter, Dark Energy is also not directly observed, but is rather from observations of gravitational interactions between cosmological bodies.
In 1915, when Albert Einstein gave his world famous paper, General Theory of Relativity, which showed the curvature of space-time on one side to the presence of energy and matter in the Universe on the other side.
In the paper, he had given in one of his ten field equations,
where G is the gravitational constant. Although this is the simplest form of the equations the freedom remains to add a constant term. This “cosmological constant” was what Einstein added in order to achieve a static universe, and it is given the symbol Λ
The cosmological constant given by Einstein was a component that would oppose the gravity in his model and keep the Universe in balance i.e. the Universe would neither expand or contrast but it applicable to a static universe only. But our Universe isn’t static, this is now considered as the biggest blunder made by Einstein.

The Universe is unstable, was proven by Russian physicist Alexander Friedmann in 1922. He found out that the cosmological constant was wrong as the Universe was not static. He assumed that the Universe is full of matter and radiation, and is curved. He also added that the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic i.e. same in all directions and at all locations. To prove these assumptions he gave two equations
and
Where, H is Hubble constant (which indicates how fast the Universe is expanding), R is scaling parameter and k is curvature parameter ( which indicates the rate of expansion of the Universe and whether or not that the expansion rate is increasing or decreasing. It also indicates the future fate of the universe.). The curvature parameter indicates whether the universe is open or closed. The above equations do not specify the nature of the density ρ.
These equations show that the Universe either contracts or expands depending on the content and rate of expansion of the Universe, which shows that it evolves with time. Thus this proved that the Universe wasn’t static but rather unstable.

The Universe is expanding, was proven by Edwin Hubble in the late 1920s. He observed that the redshift of galaxies is directly proportional to the distance of the galaxy from the observer i.e. Earth when he was studying the galaxies outside the Milky Way. This gave birth to the Hubble Law, which is now called Hubble-LeMaitre Law, which states that:
Objects observed in space with more than 10 mega parsecs (Mpc) (1 parsecs or 1 pc = 3.26156 lightyears) are found to have a redshift, interpreted as a relative velocity away from Earth;
This Doppler shift-measured velocity of various galaxies receding from the Earth is approximately proportional to their distance from the Earth for galaxies up to a few hundred mega parsecs away.
The equation is given as,
ν=Hr
Where, ν is recessional velocity (which is the rate at which an extragalactic astronomical object recedes from an observer as a result of the expansion of the universe), H is Hubble constant and r is distance.
The value of Hubble constant has varied over the years. The current value of H is 73.8 km/s per Mpc.
These two finding proved that Einstein’s cosmological constant was not applicable to our Universe. The findings were later acknowledged by Einstein himself, who considered this as a blunder.
Theories Related to Dark Energy
Cosmological Constant (Λ)
In this theory, Einstein’s blunder is said to be perfectly suitable for Dark Energy and that it is the intrinsic and fundamental energy of space. Since mass and energy are related then according to the famous equation given by Einstein that E=mc2, then his theory of general relativity predicts that this energy will have a gravitational effect. This is usually called vacuum energy as it is the energy density of an empty vacuum.
The cosmological constant has a negative pressure which is seen through classical thermodynamics, this negative pressure is equal and opposite to its energy density so due to this it causes the acceleration of the expansion of the universe. The current cosmological model i.e. the Lambda-CDM model (or the current cosmological model) includes the cosmological constant as an important feature and also the cosmological constant is the only solution for the accelerated rate of expansion of the Universe.
Quintessence
In this theory of Quintessence, the observed acceleration of the scalar factor is caused due to the potential energy of the dynamical field called the Quintessence field. This differs from the cosmological constant as it can vary with space and time. So that this doesn’t clump and form a structure like matter, the field has to be very light so that it has a very large Compton Wavelength which is equal to the wavelength of a photon whose energy is same as the mass of that particle i.e. E=hmc where his the Planck’s constant, m is mass of the particle and c is the speed of light.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy Interaction
In this theory, it is believed that dark matter and dark energy are both a single phenomenon that modifies gravity at various scales.
How will Dark Energy affect us?
Dark Energy is said to lead the Universe to any one of these three scenarios:
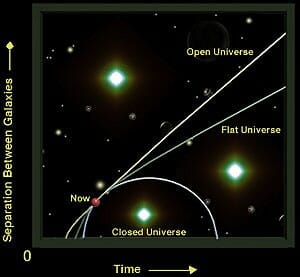
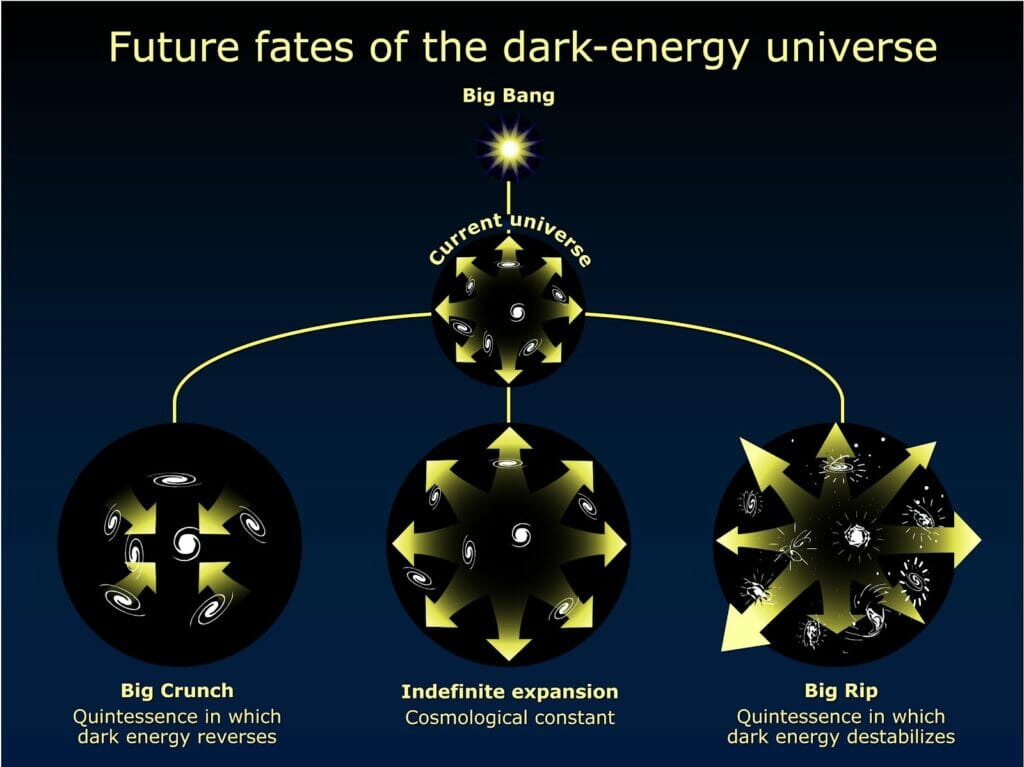
Closed Universe
In this theory, it is believed that the Universe will expand upto a certain point and stop due to gravity, but then start to contract till it reaches a point that all matter is collapsed, this is also called the Big Crunch.
Open Universe
In this theory, it is said that the universe will continue expanding at an accelerating speed. But later on, the acceleration caused by dark energy will be so strong that it overcomes the effect of gravitational, electromagnetic and strong binding force which will make the Universe to destabilize and lead it to explode. This is also called the Big Freeze or Big Rip.
Flat Universe
In this theory, the expansion of the Universe will continue and will remain stable. But it is also believed to end up like the Open Universe




Howdy! I know this is sort of off-topic however I needed to ask.
Does operating a well-established website such as yours require a large amount of
work? I’m completely new to running a blog but I do write in my journal daily.
I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and feelings online.
Please let me know if you have any suggestions or tips for new aspiring blog owners.
Appreciate it!
WOW just what I was searching for. Came here by searching for website
[…] are a few things the equation does not contain any information about. : Inflation, Dark matter, Dark energy and so […]
I think dark energy is also called “anti-gravity” because gravitional force binds the matter(micro-protons,electrons and neutrons and macro-planets,galaxies) but as we know that universe is expanding due to the observations that proved big bang theory almost correct then there must be a energy which is acting opposite to gravitional force in nature and thus this energy has been in existence since the big bang and named it dark energy which has existed since the big bang. BTW what is the difference between dark matter and dark energy?
[…] life. Under this field, they have a no. of researches like Physics of the Cosmos, Dark Matter & Dark Energy and Black Holes to name a few. The Hubble Space Telescope has been getting images from very ends of […]
[…] dark matter makes up 27% of the Universe and the remaining by another mysterious substance called Dark Energy. The only things related to dark matter is that it’s invisible, exerts a gravitational pull that […]
[…] Dark Energy is another mystery which was introduced to resolve the existing mysteries of accelerated expansion of the universe. Theories constructing models for varying dark energy could explain this discrepancy. They do this by stating that the excess of energy present in the early universe provided pressure required to accelerate the expansion. And that is the reason why we see an accelerated expansion today. But again no perfect model is present for the dark energy, thus any changes would again lead to much more discrepancies. […]
[…] present Universe we are in is currently dominated by a mysterious form of energy called Dark Energy. Observations suggest that it compromises about 73% of the total energy density of the present […]
Dark matter*
Nice article. Maybe the next article we expect is hunt for candidate of drak matter, axioms. I would appreciate if you would write about that too.
Thank you, i’ll will surely write about it. Thought the previous article of mine on Dark Matter has a small part of axions mentioned in it.